Property / Developer / Singapore district categories 3 comments

(P.S: Sorry for any disturbances the advertisements above may have caused you)
Some of this may be pretty basic to veteran property investors and yet it might be useful reference for some. As they say, in property, it's about location, location, location.
The district classification of Singapore property
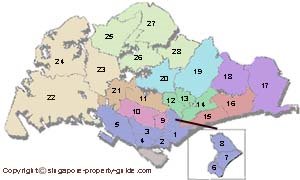
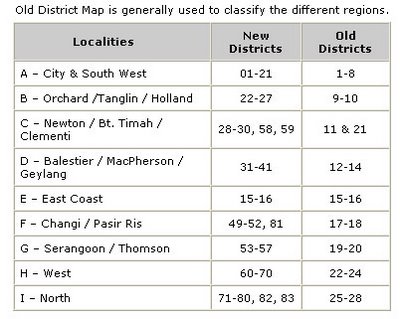
For reference, the various areas by their normal names:
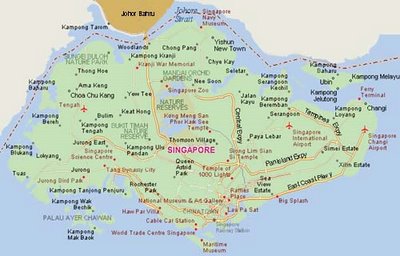
To add some value to the article from the point of residential property:
Properties in the prime districts of 9, 10 and 11 are still the most sought after. Prime developments such as Regency Park, Four Seasons Park and Nassim Jade, alltime favorites for expatriates, are located here.
Properties in districts 15 and 16 (East Coast), and 5 (Clementi and Pasir Panjang) are also popular. These locations are desirable due to their central location and proximity to shopping, recreation amenities and international schools.
For investments (rental), these are typically areas to go for, because they are popular with foreigners (who would typically be the ones renting).
References:
(1) Singaporeproperty.com
(2) Colliers April 2005 Research Paper: Singapore Residential Property Market: Investing in Residential Properties